Introduction
With its unmatched comfort, energy efficiency, and health benefits, far infrared heating has become a hot new technology in the field of heating solutions in recent years. This article explores the definition, significance, and applications of far-infrared heating, delving into its complexities.
Far Infrared Heating: What Is It?
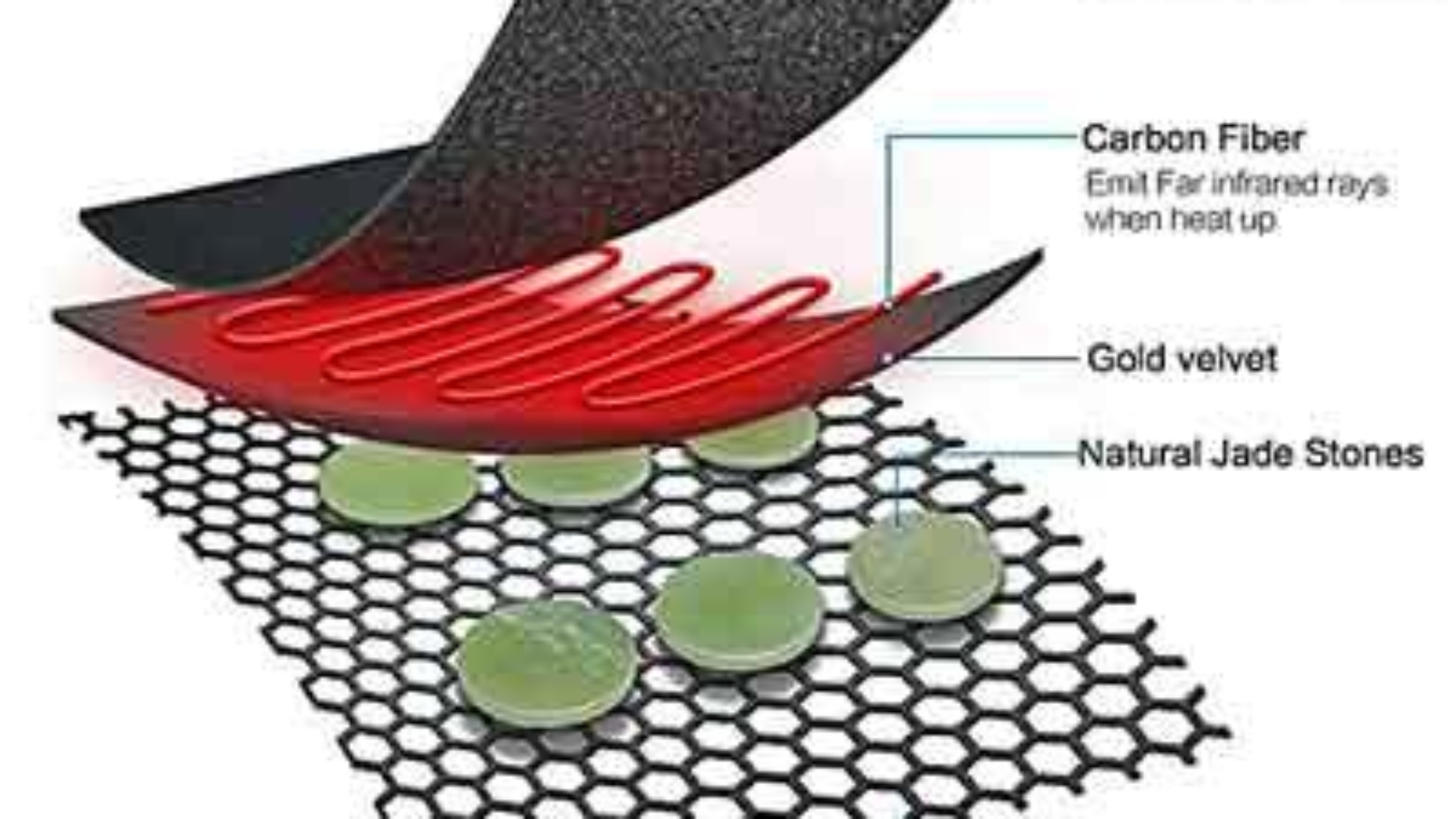
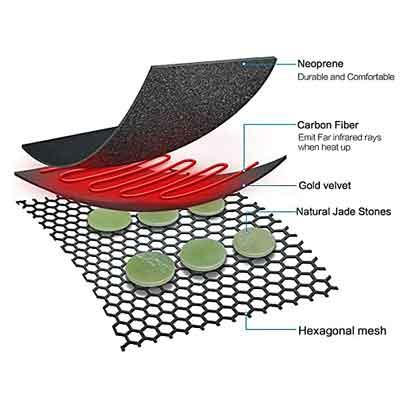
Heat is produced by far infrared heating, which uses electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from 3 to 1000 micrometers. With far infrared heating, surfaces and objects are heated directly, producing a steady and comfortable warmth, in contrast to conventional heating systems that rely on convection or conduction.
Significance and Importance
The increasing popularity of far infrared heating systems can be attributed to their many benefits over traditional heating techniques. In addition to providing warmth, far-infrared heating has therapeutic benefits, enhanced air quality, and energy efficiency for both residential and commercial spaces.
Categories and Types
There are several types of far-infrared heating systems, each designed to meet particular needs and applications. To choose the best option, it is necessary to comprehend the various types and categories.
Panel Warmers
One of the most popular types of far-infrared heating systems is the panel heater. These elegant and unobtrusive units complement the design of any room while offering effective heating. They can be freestanding or wall-mounted.
Warmth from Radiant Flooring
To provide radiant floor heating, far-infrared heating components are embedded beneath the flooring. By removing cold spots and distributing heat evenly throughout the space, this technique maximizes comfort.
Carry-Along Infrared Warmers
Users can take advantage of far-infrared heating in a variety of environments with the flexibility and convenience that portable infrared heaters provide. These small units are perfect for adding to existing heating systems or for spot heating.
Infrared heaters for outdoors
Patios, terraces, and gardens can be used for longer periods thanks to outdoor infrared heaters. Even in the colder months, these heaters’ radiant heat makes an inviting setting for al fresco dining and lounging.
Signs and Symptoms
To minimize problems and maximize comfort, it’s critical to identify the symptoms of inefficient heating systems and poor indoor air quality.
Inconsistent Heating
Having certain parts of a room stay colder than others due to uneven heating is a typical symptom of traditional heating systems. This issue is resolved by far-infrared heating, which evenly distributes heat across surfaces to provide constant warmth throughout the room.
Empty Air
The dry indoor air produced by traditional heating techniques can cause discomfort and respiratory problems. By producing soft, radiant heat that doesn’t dry out the air, far-infrared heating systems improve the comfort and health of their surroundings.
Chilled The floors
Many homes have cold floors, which is a common complaint, especially in the winter. Radiant floor heating provides opulent warmth from the ground up by installing far-infrared panels beneath the floor surface, eliminating the discomfort of cold floors.
Reasons and Danger Elements
People can choose their heating solutions more intelligently if they are aware of the risk factors and underlying causes of inefficient heating systems.
Traditional Heating Systems
Conventional heating systems lose heat through ducts, vents, and gaps in the insulation because they use forced air or convection to distribute heat. This inefficiency degrades indoor air quality in addition to increasing energy consumption.
Insufficient Insulation
Heat loss and energy inefficiency are made worse by inadequate insulation, which makes heating systems work harder to maintain desired temperatures. Making the right insulation investments is crucial to maximizing the efficiency of far-infrared heating systems and lowering energy expenses.
Impact on the Environment
In an era of climate change, there is growing concern about the environmental effects of traditional heating methods, such as the combustion of fossil fuels. A sustainable substitute is provided by far-infrared heating, which produces radiant heat without producing any hazardous emissions by using electricity.
Diagnosis and Tests
Doing diagnostic tests and evaluations to find areas for improvement is a common step in evaluating the efficacy and efficiency of heating systems.
Audits of Energy
Energy audits uncover areas for optimization and offer insightful information about a building’s usage patterns. Energy audits assist businesses and homeowners in making well-informed decisions regarding the upgrade to far-infrared heating by evaluating variables like insulation, air leakage, and heating system efficiency.
Thermography
With the use of thermal imaging technology, it is possible to see how heat is distributed throughout a room and identify any inefficient or hot spots. The use of thermal imaging helps to maximize the efficiency of far-infrared heating systems by identifying thermal anomalies, such as drafts or inadequate insulation.
Monitoring of Indoor Air Quality
Maintaining a comfortable and healthy living or working environment requires regular monitoring of the indoor air quality. By reducing dust, allergens, and airborne pollutants, far-infrared heating systems that do not rely on forced air circulation help maintain the best possible indoor air quality.
Options for Treatment
Making the switch to far-infrared heating is a proactive step toward enhancing well-being, comfort, and energy efficiency. Examine the different approaches that can be used to upgrade to far-infrared heating systems.
Refitting Current Systems
Far infrared heating technology can be retrofitted into existing infrastructure to provide a cost-effective solution for homes and businesses looking to upgrade their heating systems. Retrofitting reduces installation time and disruption by incorporating far infrared panels or elements into already-existing ductwork or heating systems.
Integration of New Construction
When far-infrared heating systems are integrated from the beginning of new construction projects, they can be easily incorporated into building layouts and architectural plans. New construction can attain maximum comfort and energy efficiency right from the beginning by carefully positioning far-infrared panels or elements throughout the building.
Control and Zoning
With the ability to precisely control and zone, far-infrared heating systems enable users to personalize the temperature in each room or space. Users can optimize energy usage and comfort levels based on occupancy and usage patterns by creating zones within the space and installing independent controls for each zone.
Preventive Actions
Preventive maintenance is essential for optimizing far-infrared heating systems’ lifespan and performance while reducing problems and interruptions.
Continual Upkeep
For far-infrared heating systems to remain reliable and efficient, regular maintenance and inspections are necessary. Cleaning panels, testing connections, and examining controls are a few examples of tasks that assist in locating possible problems early on and addressing them.
Management of Air Quality
For far-infrared heating systems to function properly, optimal indoor air quality must be maintained. To maintain clean and healthy air circulation throughout the space, dust, allergens, and pollutants cannot build up due to routine cleaning of air filters, ventilation systems, and ductwork.
Monitoring of Temperature
Users can quickly detect inefficiencies or irregularities in far-infrared heating systems by keeping an eye on temperature levels and patterns. Users can monitor the performance of their heating system and make necessary adjustments to maintain comfort and energy efficiency by using temperature monitoring devices or smart thermostats.
Conclusion
In conclusion, far infrared heating represents a transformative innovation in the realm of heating technology, offering unmatched comfort, energy efficiency, and health benefits. From residential spaces to commercial establishments, the adoption of far infrared heating systems promises to revolutionize the way we heat our homes and workplaces, ushering in a new era of sustainability and comfort.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Far Infrared Heating
Is it safe to use far-infrared heating systems?
In truth, when installed and operated properly, far-infrared heating systems are safe. While far infrared radiation is entirely safe and has been used for decades in a variety of therapeutic applications, ultraviolet (UV) radiation can be hazardous in high doses. Far infrared heating systems are a safe and pleasant heating option for homes and businesses since they don’t produce dry air or release hazardous emissions.
Would far-infrared heating save money on heating bills?
Yes, by maximizing energy efficiency and minimizing heat loss, far-infrared heating can contribute to lower heating costs. In contrast to conventional heating systems, which frequently cause heat to escape through ducts, vents, and insulation gaps, far-infrared heating heats objects and surfaces directly, guaranteeing that the heat produced stays in the area. Over time, considerable energy savings can result from this targeted heating strategy.
Which kinds of spaces work well with far-infrared heating?
Many different types of spaces, such as residences, workplaces, warehouses, and commercial buildings, are appropriate for far infrared heating. Far infrared heating systems are adaptable enough to fit the unique heating needs of any setting, be it a single room, a whole building, or outdoor spaces like patios and terraces.
Do far-infrared heating systems have a positive environmental impact?
Yes, when compared to conventional heating techniques that depend on combustion or fossil fuels, far-infrared heating systems are more environmentally friendly. Far-infrared heating systems use electricity to create radiant heat, which results in zero emissions and helps lower carbon footprints. Furthermore, far-infrared heating’s energy efficiency reduces environmental impact and helps conserve resources.
What is the lifespan of infrared heating systems?
The average lifespan of far-infrared heating systems is 20 to 30 years or longer, depending on usage and maintenance. These systems are made to be strong and long-lasting. Far infrared heating manufacturers make sure that their systems operate dependably and efficiently for many years by investing in high-quality parts and materials.